IEEE ACCESSに1件採択

IEEE ACCESSに下記の論文が採択されました。
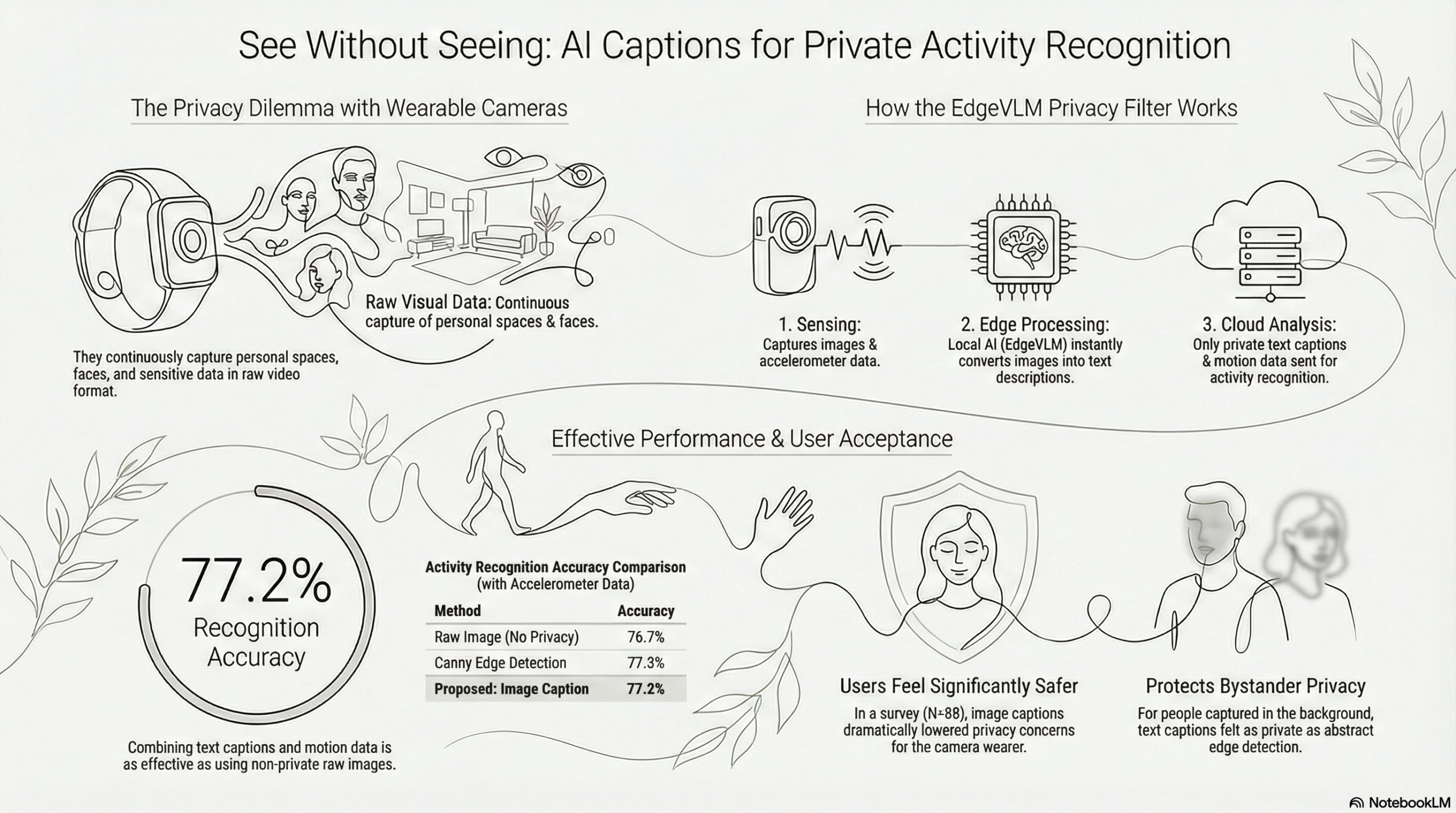
この論文は、ウェアラブルカメラを用いた人間活動認識(HAR)における、プライバシー保護と認識精度のトレードオフを解決するための新しいアプローチを提案しています。従来のカメラベースの手法では、生活環境の豊かなコンテキストを取得できる反面、顔や機密情報が記録されるリスクがあり、一方で過度な匿名化(ぼかし処理など)は認識に必要な特徴を損なうという課題がありました。
そこで本研究では、エッジデバイス上で動作する軽量な視覚言語モデル(EdgeVLM)を「プライバシーフィルタ」として導入しました。この手法は、映像をローカルで意味のあるテキスト(画像キャプション)に変換し、生画像を即座に破棄することで「データ最小化」を実現し、外部への漏洩リスクを最小限に抑えます。さらに、このテキスト情報と加速度センサデータを統合したマルチモーダルモデルを構築することで、視覚的な特徴を意味的なテキスト情報で代替する仕組みを提案しました。
Koushi Hiraoka, Yugo Nakamura, Yutaka Arakawa EdgeVLM as a Privacy Filter: Towards Privacy-Aware Activity Recognition from Wearable Camera Using Image Captions Journal Article In: IEEE Access, 2026.@article{11367700,
title = {EdgeVLM as a Privacy Filter: Towards Privacy-Aware Activity Recognition from Wearable Camera Using Image Captions},
author = {Koushi Hiraoka, Yugo Nakamura, Yutaka Arakawa},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2026.3659343},
doi = {10.1109/ACCESS.2026.3659343},
year = {2026},
date = {2026-01-27},
journal = {IEEE Access},
abstract = {Egocentric video captured by wearable cameras offers rich contextual information for recognizing human activities in daily life. However, such video often includes sensitive personal details that must be protected from external threats. This creates a fundamental trade-off between preserving data utility and ensuring privacy, particularly in scenarios where continuous activity monitoring is required. In this study, we explore the concept of using EdgeVLM—a vision-language model designed to run entirely on edge devices—as a privacy filter for wearable camera data. We investigate the impact of caption granularity and demonstrate that our method locally transforms egocentric video into semantically rich textual image captions, enabling activity detection without transmitting raw visual content to the cloud. This edge-based processing preserves contextual cues while minimizing privacy risks through data minimization. To evaluate this approach, we conducted a quantitative user study (N=88) that found EdgeVLM-generated captions notably decreased participants’ privacy concerns compared to raw, blurred, or cartoonized images. Critically, from a bystander’s perspective, the proposed method demonstrated privacy protection levels statistically comparable to canny edge detection. Additionally, when combined with accelerometer data, the caption-based method achieved a 77.2% accuracy in recognizing desk activities such as typing, mousing, swiping, drinking, and writing—effectively replacing pixel-level visual information with text while maintaining performance comparable to models using unfiltered visuals. These findings indicate that EdgeVLM-based image captioning is a promising privacy-conscious solution for wearable camera applications, facilitating continuous activity recognition while protecting user privacy at the edge.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}


