国際ジャーナル「IEEE Access」に1件採択
2023年11月4日 最終更新日時 : 2023年11月6日 report
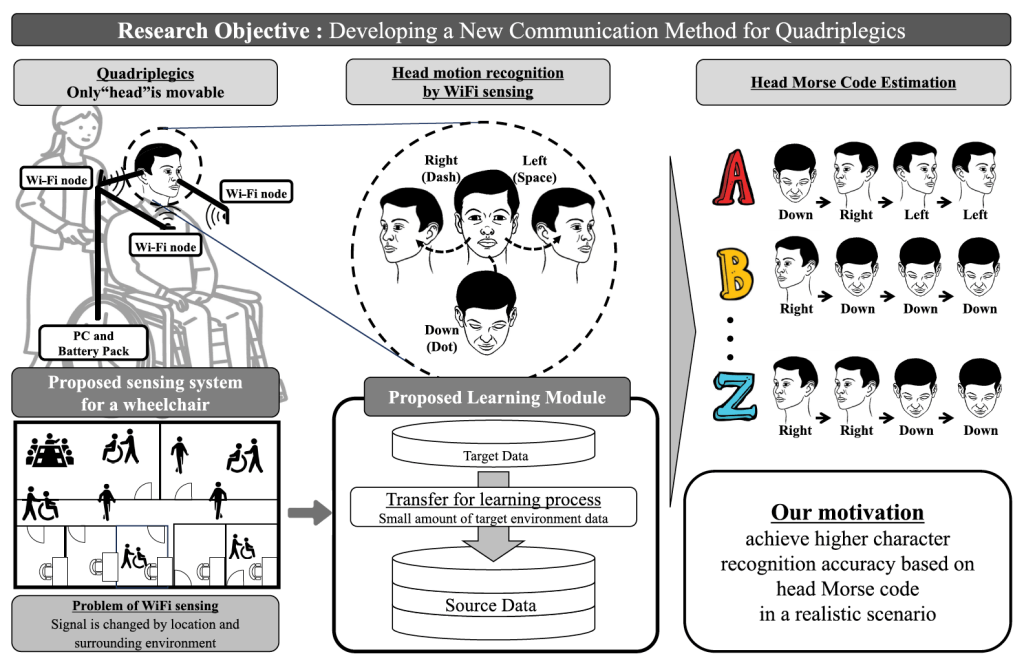
国際ジャーナル 「IEEE Access」 に下記の論文が採択されました.
Marwa R. M. Bastwesy, Hyuckjin Choi, Yutaka Arakawa
HeMoFi4Q: Morse Communication Based on Wi-Fi and Head Motion for Quadriplegia With Environmental Robustness Journal Article
In: IEEE Access, vol. 11, pp. 116384-116397, 2023, ISSN: 2169-3536.
@article{access2023-bastwesy,
title = {HeMoFi4Q: Morse Communication Based on Wi-Fi and Head Motion for Quadriplegia With Environmental Robustness},
author = {Marwa R. M. Bastwesy, Hyuckjin Choi, Yutaka Arakawa},
doi = {10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3326259},
issn = {2169-3536},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-10-20},
urldate = {2023-10-20},
journal = {IEEE Access},
volume = {11},
pages = {116384-116397},
abstract = {Quadriplegics face a communication obstacle as their physical abilities are restricted, leaving them unable to speak or use their limbs, with only their upper neck being mobile. So, we propose a recognition system and a new communication language utilizing Morse code and head movements, to break this barrier. We aim to overcome the limitations of camera-based and wearable-sensor methods, including occlusion, privacy concerns, and user inconvenience. The goal is to passively detect quadriplegics’ head movements and map them to their corresponding character. The dataset including all 26 alphabet letters, was gathered in various settings, including single-user and multi-human environments, with multiple locations for each setting. For evaluation, 2% samples are randomly selected from the unseen environment to be used with the seen environment as a training dataset. Based on the results, our system demonstrates practical feasibility for real-world implementation, with accuracy rates of 94% and 80% achieved in single-user and multi-human environments, respectively.HeMoFi4Q: Morse Communication Based on Wi-Fi and Head Motion for Quadriplegia With Environmental Robustness},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Quadriplegics face a communication obstacle as their physical abilities are restricted, leaving them unable to speak or use their limbs, with only their upper neck being mobile. So, we propose a recognition system and a new communication language utilizing Morse code and head movements, to break this barrier. We aim to overcome the limitations of camera-based and wearable-sensor methods, including occlusion, privacy concerns, and user inconvenience. The goal is to passively detect quadriplegics’ head movements and map them to their corresponding character. The dataset including all 26 alphabet letters, was gathered in various settings, including single-user and multi-human environments, with multiple locations for each setting. For evaluation, 2% samples are randomly selected from the unseen environment to be used with the seen environment as a training dataset. Based on the results, our system demonstrates practical feasibility for real-world implementation, with accuracy rates of 94% and 80% achieved in single-user and multi-human environments, respectively.HeMoFi4Q: Morse Communication Based on Wi-Fi and Head Motion for Quadriplegia With Environmental Robustness


